Introduction to Computers/Computer Hardware
Hardware refers to the physical parts or components of a computer. Hardware includes components such as the monitor, keyboard, hard drive disk, mouse, printers, graphic cards, sound cards, memory, motherboard and chips, etc.
Hardware Components of a Computer
- CPU
- Power Supply
- RAM
- Storage
- Optical drive
- Hard drive
- Solid state drive
- Expansion cards
- Video card
- Audio card
- Network card
- Modem
- Motherboard/mainboard
- System cooling
- Case fans
- CPU fans
- Liquid cooling
- The central processing unit, or CPU, is that part of a computer which executes software program instructions.
- The power supply unit, or PSU, converts general purpose electric current from the mains to direct current for the other components of the computer
- A PC’s main memory is a fast storage area that is directly accessible by the CPU, and is used to store the currently executing program and immediately needed data. PCs use semiconductor random access memory (RAM) of various kinds such as DRAM, SDRAM or SRAM as their main memory.
- Mass storage devices such as hard drives store programs and data even when the power is off; they do require power to perform read and write functions during usage.
- Optical drives, including CD, DVD, and Blu-ray Disc, are data storage devices using rapidly rotating discs coated with reflective material and read using a laser diode.
- Hard disk drives (HDD) are data storage devices used for storing and retrieving digital information using rapidly rotating disks (platters) coated with magnetic material
- Solid state drives (SSD) are data storage devices using integrated circuit assemblies as memory to store data persistently.
- Video cards—otherwise called graphics cards, graphics adapters or video adapters—process the graphics output from the motherboard and transmit it to the display.
- Audio cards are internal computer expansion cards that facilitate economical input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs, also known as a sound card.
- A network interface controller (NIC, also known as a network interface card, network adapter, LAN adapter, and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.
- A modem (modulator-demodulator) is a device that modulates signals to encode digital information and demodulates signals to decode the transmitted information, initially used for telephone line data transmission, but also used with DSL and cable high speed connections.
- The motherboard, also referred to as system board or main board, is the primary circuit board within a personal computer, and other major system components plug directly onto or cable into the motherboard.
- System cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits. Methods include case fans, CPU fans, and liquid cooling.
- Liquid cooling uses a liquid rather than air as the heat conductor, with the most common heat transfer fluid in desktop PCs being (distilled) water.
- The fundamental purposes of the BIOS are to initialize and test the system hardware components, and to load a boot loader or an operating system from a mass storage device.
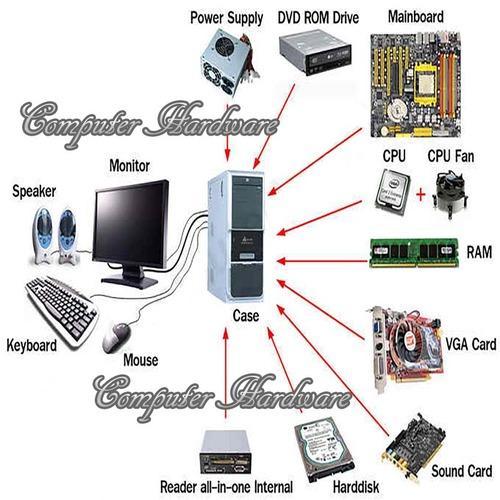
Figure: Computer Hardware
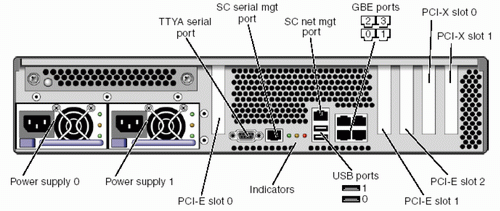
Figure: Computer (Server) Ports
